Masterfully Deciphering 3 Crucial Financial Statements: A Powerful Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Masterfully Deciphering 3 Crucial Financial Statements: A Powerful Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Masterfully Deciphering 3 Crucial Financial Statements: A Powerful Guide
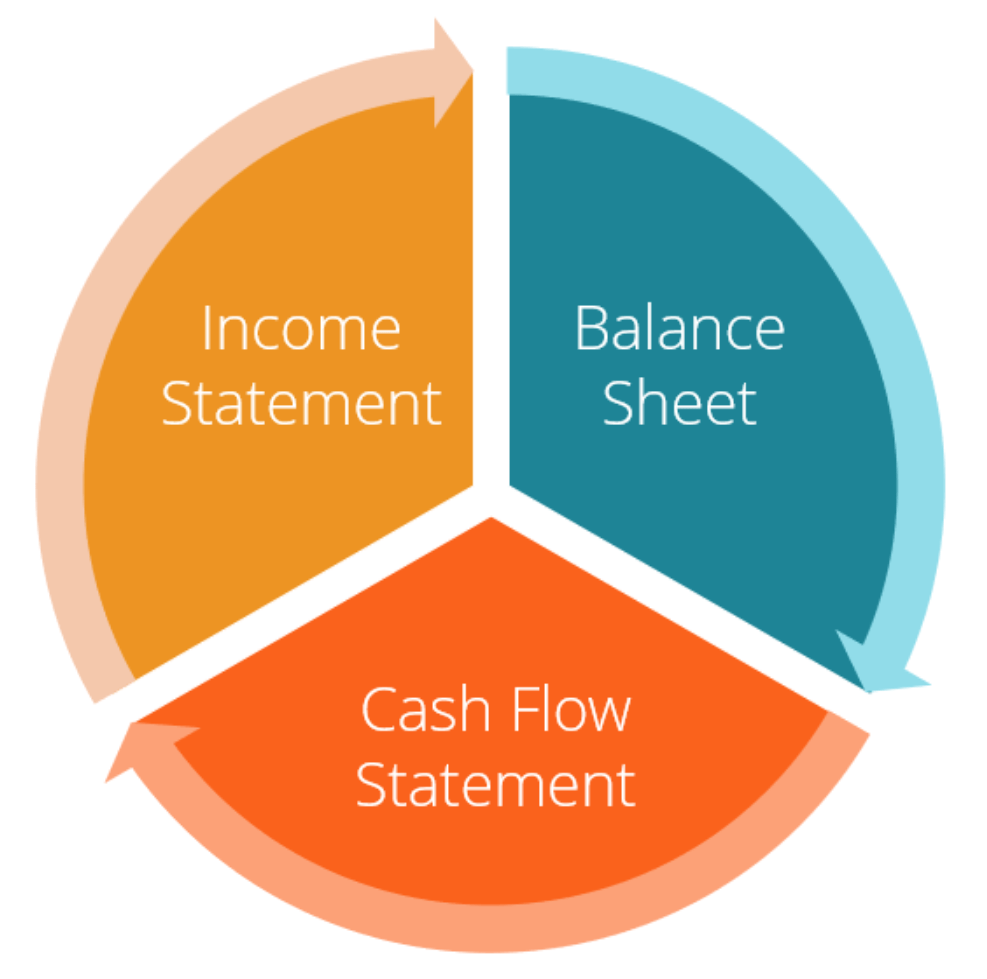
Understanding a company’s financial health can feel like navigating a dense jungle. But armed with the right knowledge, you can confidently traverse this terrain and extract valuable insights. This article provides a powerful guide to understanding three crucial financial statements: the balance sheet, the income statement, and the cash flow statement. Mastering these will empower you to make informed decisions, whether you’re an investor, entrepreneur, or simply seeking to improve your financial literacy.
The Balance Sheet: A Snapshot in Time
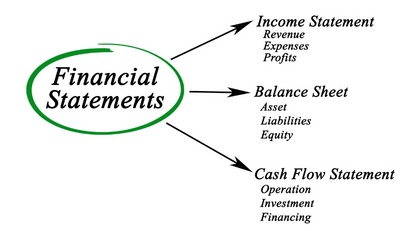
The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It adheres to the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Let’s break down each component:
-
Assets: These are what a company owns, representing resources that have economic value. Assets are categorized into current assets (those expected to be converted to cash within a year) and non-current assets (long-term assets). Examples of current assets include cash, accounts receivable (money owed to the company), and inventory. Non-current assets include property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), intangible assets (patents, copyrights), and long-term investments.
-
Liabilities: These represent a company’s obligations or debts. Like assets, liabilities are categorized into current liabilities (due within a year) and non-current liabilities (due beyond a year). Examples of current liabilities include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), short-term loans, and salaries payable. Non-current liabilities include long-term loans, bonds payable, and deferred revenue.
-
Equity: This represents the owners’ stake in the company. It’s the residual interest in the assets after deducting liabilities. For corporations, equity includes common stock (representing ownership shares), retained earnings (accumulated profits reinvested in the business), and additional paid-in capital. For sole proprietorships and partnerships, equity is simply the owner’s capital.
Analyzing the balance sheet involves assessing the company’s liquidity (ability to meet short-term obligations), solvency (ability to meet long-term obligations), and capital structure (mix of debt and equity financing). Key ratios derived from the balance sheet include the current ratio (current assets / current liabilities), which measures short-term liquidity, and the debt-to-equity ratio (total debt / total equity), which indicates the company’s reliance on debt financing. A high debt-to-equity ratio can signal higher risk.

The Income Statement: Performance Over Time
Unlike the balance sheet, the income statement shows a company’s financial performance over a period of time (e.g., a quarter or a year). It follows a basic structure:
-
Revenue: This represents the total income generated from the company’s primary operations. It’s often referred to as sales or turnover.

-
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This represents the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services sold. For a manufacturing company, this includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. For a service company, this might include salaries of service providers and direct expenses.
-
Gross Profit: This is calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue. It represents the profit earned before considering operating expenses.
-
Operating Expenses: These are the costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and administrative expenses.
-
Operating Income (EBIT): This is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the company’s core operations.
-
Interest Expense: This is the expense incurred on debt financing.
-
Income Before Taxes: This is calculated by subtracting interest expense from operating income.
-
Income Tax Expense: This is the tax liability incurred on the company’s taxable income.
-
Net Income: This is the final profit after deducting all expenses, including taxes. It represents the bottom line of the income statement.
Analyzing the income statement involves examining revenue growth, profitability margins (gross profit margin, operating profit margin, net profit margin), and expense control. Trends in these metrics over time provide valuable insights into the company’s performance and efficiency.
The Cash Flow Statement: The Movement of Cash
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash both into and out of a company over a period of time. It’s divided into three main sections:
-
Operating Activities: This section reflects cash flows from the company’s core business operations. It includes cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, and cash paid for operating expenses. The indirect method is commonly used, starting with net income and adjusting for non-cash items (like depreciation and changes in working capital).
-
Investing Activities: This section reflects cash flows related to investments in long-term assets. It includes cash spent on purchasing PP&E, investments in other companies, and proceeds from the sale of assets.
-
Financing Activities: This section reflects cash flows related to financing the business. It includes cash from issuing debt or equity, cash paid for debt repayments, and cash paid for dividends.
Analyzing the cash flow statement is crucial for understanding a company’s liquidity and its ability to generate cash. A positive cash flow from operating activities indicates strong operational efficiency. The statement also reveals how the company is financing its growth and managing its debt. Key metrics include free cash flow (cash flow from operations minus capital expenditures), which represents the cash available for distribution to shareholders or reinvestment in the business.
Putting it All Together: A Holistic View
By analyzing these three statements together, you gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. The income statement shows the company’s performance over a period, highlighting profitability and revenue growth. The cash flow statement reveals the company’s cash inflows and outflows, providing insights into its liquidity and ability to generate cash.
Understanding these statements is not merely an accounting exercise; it’s a crucial skill for anyone involved in making financial decisions. Whether you are evaluating an investment opportunity, managing your own finances, or running a business, the ability to interpret these statements effectively is a powerful tool that can lead to better outcomes. Remember, consistent practice and a willingness to delve deeper into the details will significantly enhance your understanding and ability to extract meaningful insights from these essential financial documents. Don’t be intimidated by the complexity; break it down step-by-step, and you’ll soon master the art of deciphering financial statements.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Masterfully Deciphering 3 Crucial Financial Statements: A Powerful Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
google.com