The Ultimate Guide to 10 Crucial Differences: Personal Loan vs Credit Card
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ultimate Guide to 10 Crucial Differences: Personal Loan vs Credit Card. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
The Ultimate Guide to 10 Crucial Differences: Personal Loan vs Credit Card
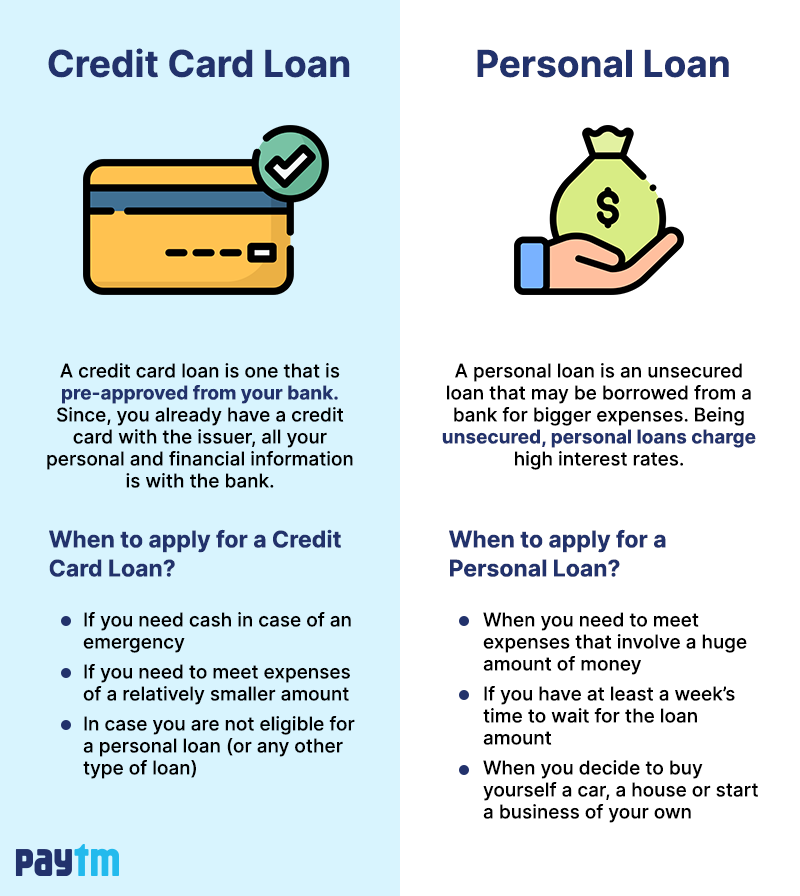
Choosing the right financial tool can be a daunting task, especially when faced with the seemingly similar options of a personal loan and a credit card. Both offer access to funds, but their underlying mechanisms, benefits, and drawbacks differ significantly. This comprehensive guide will dissect 10 key distinctions between personal loans and credit cards, empowering you to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and circumstances.
1. Access to Funds:
Personal Loan: A personal loan provides a lump sum of money upfront, typically disbursed directly into your bank account. This upfront disbursement offers immediate access to funds for specific purposes like debt consolidation, home renovations, or medical expenses.
Credit Card: Credit cards offer a revolving line of credit, allowing you to borrow funds as needed, up to a pre-determined credit limit. This flexibility provides ongoing access to funds for everyday purchases, travel expenses, or unexpected emergencies.
2. Interest Rates:
Personal Loan: Personal loans typically have fixed interest rates, meaning the interest rate remains constant throughout the loan term. This predictable rate provides financial stability and allows for accurate budgeting. However, personal loan interest rates can be higher than credit card interest rates, especially for borrowers with lower credit scores.
Credit Card: Credit cards usually have variable interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions and your creditworthiness. This variable rate can be advantageous if interest rates decline, but it can also lead to unexpected increases in your monthly payments. Additionally, credit card interest rates are generally higher than personal loan rates, making them less attractive for large, long-term expenses.
3. Repayment Terms:
Personal Loan: Personal loans have fixed repayment terms, typically ranging from 12 to 84 months. This structured repayment plan provides clear deadlines and allows for consistent budgeting. However, longer loan terms can lead to higher overall interest costs.
Credit Card: Credit cards offer a minimum monthly payment based on your outstanding balance. While this flexibility allows for lower monthly payments, it can also lead to extended repayment periods and increased interest accumulation. Additionally, carrying a balance on your credit card can significantly impact your credit score.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pros-cons-personal-loans-vs-credit-cards-v1-4ae1318762804355a83094fcd43edb6a.png)
4. Fees:
Personal Loan: Personal loans may involve various fees, including origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment fees. It’s crucial to understand these fees upfront to calculate the true cost of borrowing.
Credit Card: Credit cards can also have fees, including annual fees, balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, and late payment fees. The specific fees associated with your credit card will depend on the issuer and the card type.
5. Credit Score Impact:
Personal Loan: Taking out a personal loan can impact your credit score both positively and negatively. A successful repayment history can improve your credit score, while missed payments can damage it.

Credit Card: Credit card usage can have a significant impact on your credit score. Responsible use, including paying your balance in full each month and keeping your utilization rate low, can positively influence your score. However, carrying a balance and missing payments can negatively affect your credit score.
6. Debt Consolidation:
Personal Loan: Personal loans are often used for debt consolidation, combining multiple high-interest debts into a single, lower-interest loan. This strategy can simplify your finances and potentially save you money on interest payments.
Credit Card: While credit cards can be used to transfer balances, it’s important to note that balance transfer fees and variable interest rates can negate any potential savings. Moreover, transferring balances without addressing the underlying spending habits can lead to further debt accumulation.
7. Emergency Funds:

Personal Loan: Personal loans are generally not recommended for emergency funds. The application and approval process can take time, and the interest charges can be substantial.
Credit Card: Credit cards can serve as a valuable emergency fund, providing quick access to funds for unexpected expenses. However, it’s crucial to use them responsibly and avoid carrying a balance for extended periods.
8. Rewards and Benefits:
Personal Loan: Personal loans typically do not offer rewards or benefits. The primary purpose is to provide a lump sum of money for a specific purpose.
Credit Card: Credit cards often offer rewards programs, such as cash back, travel miles, or points. These rewards can provide valuable benefits, but it’s essential to choose a card that aligns with your spending habits and rewards structure.
9. Flexibility and Control:
Personal Loan: Personal loans offer limited flexibility. Once you receive the funds, you can only use them for the specified purpose.
Credit Card: Credit cards provide greater flexibility, allowing you to make purchases, withdraw cash, and transfer balances as needed. However, this flexibility can also lead to overspending and debt accumulation if not managed carefully.
10. Application and Approval Process:
Personal Loan: Personal loan applications typically involve a more thorough review process, including credit checks and income verification. This process can take several days or even weeks for approval.
Credit Card: Credit card applications are generally simpler and faster, often providing instant approval. However, the credit limit offered may be lower than anticipated, depending on your creditworthiness.
Conclusion:
Choosing between a personal loan and a credit card ultimately depends on your individual financial needs and goals. Personal loans offer a structured and predictable repayment plan with fixed interest rates, making them suitable for large, one-time expenses. Credit cards provide flexibility and rewards, but their variable interest rates and potential for overspending require careful management.
By carefully analyzing the 10 key differences outlined above, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial situation and empowers you to achieve your financial goals. Remember, responsible borrowing and a clear understanding of the terms and conditions are essential for maximizing the benefits of any financial tool.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ultimate Guide to 10 Crucial Differences: Personal Loan vs Credit Card. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
google.com