The Ultimate Guide to Choosing: 5 Key Differences Between Credit Unions and Banks
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ultimate Guide to Choosing: 5 Key Differences Between Credit Unions and Banks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing: 5 Key Differences Between Credit Unions and Banks
Choosing where to bank is a crucial financial decision. While both credit unions and banks offer financial services, they operate under different structures and priorities. This can lead to significant differences in fees, interest rates, and overall customer experience. Understanding these differences is essential to making the best choice for your individual needs.
1. Ownership and Mission:
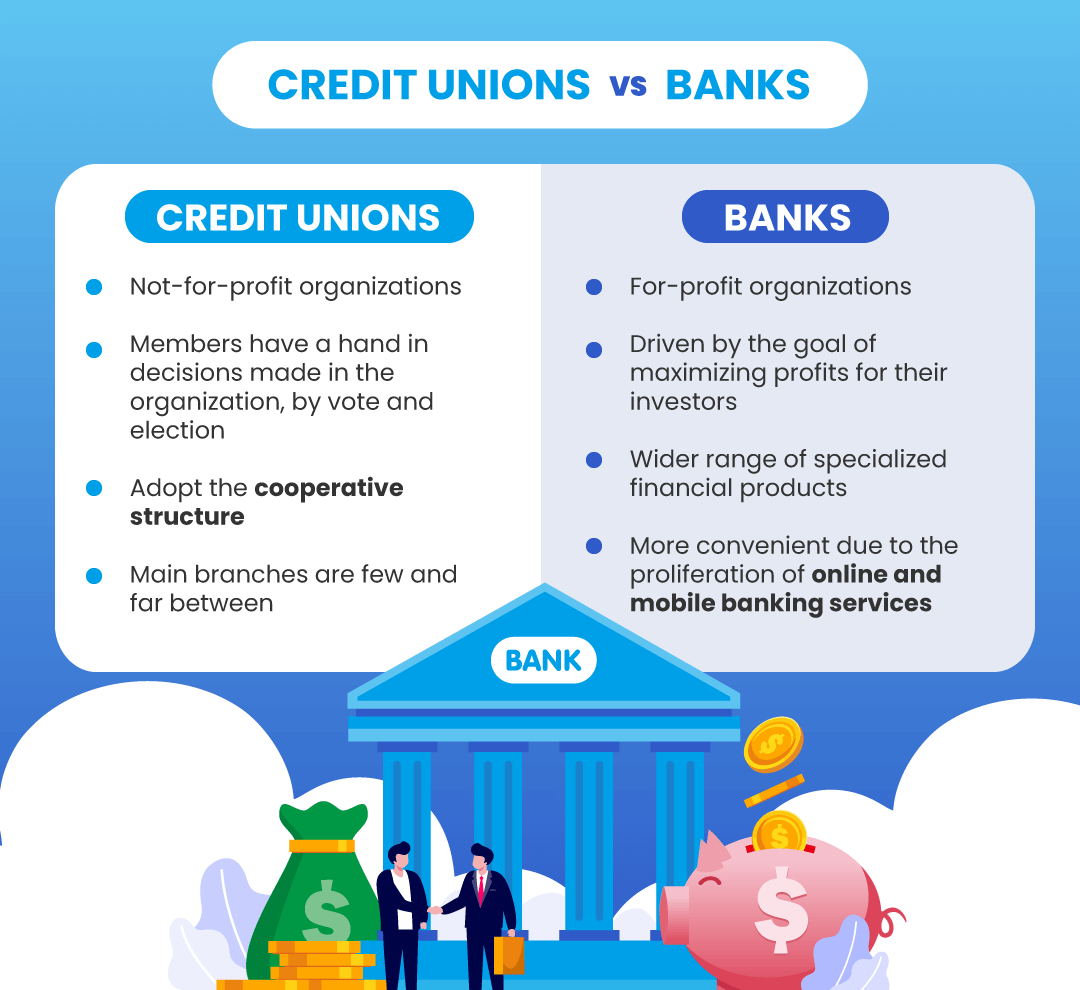
This is perhaps the most fundamental distinction between credit unions and banks. Banks are for-profit institutions owned by shareholders. Their primary goal is to maximize profits for these shareholders. Credit unions, on the other hand, are not-for-profit organizations owned by their members. This means that credit unions are ultimately accountable to their members, who are also their customers.
Credit Unions:
- Owned by members: Members have a say in how the credit union is run through voting rights and participation in board elections.
- Not-for-profit: Profits are reinvested back into the credit union to benefit members through lower fees, higher interest rates on savings, and better loan terms.
- Community focus: Credit unions often prioritize serving the needs of their local communities.
Banks:

- Owned by shareholders: Shareholders receive dividends based on the bank’s profitability.
- For-profit: Profit maximization is a key driver of decision-making.
- Broader reach: Banks typically have a larger network of branches and ATMs, making them more accessible to a wider range of customers.

2. Fees and Interest Rates:
The not-for-profit structure of credit unions often translates into lower fees and better interest rates for members. While banks may offer competitive rates to attract customers, their fees can be higher, especially on things like overdraft protection and ATM withdrawals.
Credit Unions:
- Lower fees: Credit unions generally charge lower fees for services like checking accounts, debit cards, and overdraft protection.
- Higher interest rates on savings: Credit unions often offer more favorable interest rates on savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- Lower interest rates on loans: Credit unions may offer lower interest rates on loans, particularly for mortgages and auto loans.

Banks:
- Higher fees: Banks typically charge higher fees for various services, including overdraft protection, monthly maintenance fees, and ATM withdrawals.
- Lower interest rates on savings: Banks may offer lower interest rates on savings accounts and CDs.
- Higher interest rates on loans: Banks often charge higher interest rates on loans, especially for credit cards and personal loans.
3. Loan Approval and Customer Service:
Credit unions are often known for their personalized approach to lending and customer service. They may be more likely to approve loans for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit scores, as they prioritize the needs of their members.
Credit Unions:
- Personalized service: Credit unions typically have smaller branches and a more personalized approach to customer service.
- More lenient lending criteria: Credit unions may be more flexible with loan approvals, considering factors beyond just credit scores.
- Stronger community ties: Credit unions often have a deeper understanding of the local economy and the needs of their members.
Banks:
- Standardized service: Banks typically have a more standardized approach to customer service, with a focus on efficiency and speed.
- Stricter lending criteria: Banks often have stricter lending criteria, focusing on credit scores and debt-to-income ratios.
- Less emphasis on community: Banks may have less of a focus on community involvement and may not be as responsive to the needs of individual customers.
4. Access and Convenience:
Banks typically have a larger network of branches and ATMs, making them more convenient for customers who travel frequently or need access to cash in different locations. Credit unions, on the other hand, may have a more limited network, especially in rural areas.
Credit Unions:
- Smaller network: Credit unions often have fewer branches and ATMs, which can limit convenience for some customers.
- Shared branching networks: Many credit unions participate in shared branching networks, allowing members to access services at other credit union branches.
- Online and mobile banking: Credit unions are increasingly offering online and mobile banking services, providing convenient access to accounts and services.
Banks:
- Larger network: Banks typically have a wider network of branches and ATMs, making them more accessible to a wider range of customers.
- 24/7 access: Banks often offer 24/7 access to accounts and services through online and mobile banking platforms.
- Global reach: Some banks have a global presence, providing access to services in multiple countries.
5. Products and Services:
Both credit unions and banks offer a wide range of financial products and services, including checking and savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment options. However, there may be variations in the specific products and services offered by each institution.
Credit Unions:
- Focused on core services: Credit unions often focus on providing essential financial services like checking and savings accounts, loans, and credit cards.
- Limited investment options: Credit unions may have a more limited selection of investment options compared to banks.
- Community-specific services: Some credit unions offer specialized services tailored to the needs of their local communities.
Banks:
- Wider range of products: Banks typically offer a wider range of financial products and services, including investment accounts, brokerage services, and insurance.
- More complex services: Banks may offer more complex financial products and services, such as trust accounts and estate planning.
- Global investment opportunities: Banks may offer access to global investment markets and international financial services.
Choosing the Right Option:
The best choice between a credit union and a bank ultimately depends on your individual needs and priorities. Consider the following factors:
- Fees and interest rates: Compare fees and interest rates on checking and savings accounts, loans, and credit cards.
- Loan approval criteria: If you have a less-than-perfect credit score, a credit union may be a better option.
- Access and convenience: Consider the location of branches and ATMs, as well as the availability of online and mobile banking services.
- Product and service offerings: Determine if the institution offers the specific financial products and services you need.
- Customer service: Read reviews and testimonials to get an idea of the customer service experience at each institution.
Conclusion:
Both credit unions and banks offer valuable financial services. Credit unions prioritize the needs of their members and often offer lower fees and better interest rates. Banks, on the other hand, may offer a wider range of products and services and have a larger network of branches and ATMs. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual financial goals and priorities. By carefully considering the factors outlined above, you can make an informed decision and choose the financial institution that best meets your needs.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ultimate Guide to Choosing: 5 Key Differences Between Credit Unions and Banks. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
google.com